

Next: About this document ...
Up: Numbers
Previous: B. Associativity and Distributivity
Index
A
| B
| C
| D
| E
| F
| G
| H
| I
| J
| K
| L
| M
| N
| O
| P
| Q
| R
| S
| T
| U
| W
| Z
- A
- absolute convergence
- 11.4
- absolute summability
- 11.4
- absolute value, of complex number
- 6.1
- absolute value, product formula
- 2.7
- absolute value, quotient formula for
- 2.7
- absolute value
- 2.7
- addition (field operation)
- 2.3
- addition in
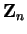
- 2.2
- addition laws for sine and cosine
- 12.6
- addition of inequalities
- 2.6
- Alembert, Jean (1717-1783)
- 11.4
- alternating series
- 11.3
- alternating series test
- 11.3
- ambiguous,
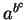
- 12.1
- ambiguous, sequence notation
- 5.1
- and, logical connective
- 1.2
- Archimedean property
- 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.2 | 5.3
- Archimedes
- 5.3
- argument(of a complex number
- 12.6
- Aristotle (384-322 B.C.)
- 2.3
| 3.2
- Arnold cats
- 6.5
- Arnold, Vladimir (1937-??)
- 6.5
- Ars Magna
- 4.2
- Artin, Emil (1898-1962)
- 2.7
- associative operation
- 2.1
- associative
- 2.2
- associativity of
- B.
- associativity of
- 4.1
| B.
- axiom, completeness
- 5.2
- axioms for a field
- 2.3
- axioms, for ordered field
- 2.6
- axioms
- intro
- axis, imaginary
- 6.2
- axis, real
- 6.2
- B
- Bernoulli, Jacob (1654-1705)
- 2.3
| 11.4 | 11.4 | 12.9
- between
- 9.2
- Bhaskara (born 1114-1185)
- 3.1
- binary operation
- 2.1
- binary search sequence
- 5.1
- Bolzano, Bernhard, (1781-1848)
- 9.2
- Boole, George (1815-1864)
- 2.2
- bound for a function
- 8.3
- bound for a set
- 8.3
- bound for sequence
- 7.5
- bound, lower
- 7.8
- bound, upper
- 7.8
- bounded function
- 8.3
- bounded sequence
- 7.5
| 7.5
- bounded set
- 8.3
- boundedness theorem
- 9.1
- bug
- 2.2
- Buhler, Joe (1950-??)
- intro
- C
- calculator operations
- 2.2
- cancellation law
- 2.1 | 2.4
- Cardano, Girolamo (1501-1576)
- 2.7 | 4.2
- Cartesian product
- 1.4
- cat, Arnold
- 6.5
- cat, discontinuous image of
- 8.3
- cat, exponential of
- 12.6
- cat, inverse of
- 6.5
- cat, square of
- 6.5
- Cauchy, Augustin(1789-1857)
- 3.5
| 4.2
| 9.2
- chain rule
- 10.1
- circle of convergence
- 12.2
- circle,unit
- 6.2
- circle
- 6.2
- Clenias
- 3.2
- closed interval
- 5.1
- codomain of function
- 1.5
- commensurable
- 3.2
- commutative operation
- 2.1
- commutative
- 2.2
- commutativity of addition in field
- 2.4
- comparison test (limit)
- 11.2
- comparison test for series
- 11.2
- comparison theorem for null sequences
- 7.3
- complete
- 5.2
- completeness axiom
- 5.2
- completeness
- 5.3
- complex conjugate
- 4.2
- complex function
- 8.1
- complex numbers
- 6.1
- complexification
- 4.1
- composition of continuous functions
- 8.2
- composition of functions
- 8.2
- composition
- 8.1
- conjugate, complex
- 4.2
- conjugate
- 4.2
- constant sequence
- 7.1 | 7.2
- continuity of
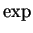 , (in theorem 12.27)
, (in theorem 12.27) - 12.4
- continuity of roots
- 8.2
- continuity, of
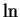
- 12.5
- continuity
- 5.3
- continuous at a point
- 8.2
- continuous on a set
- 8.2
- continuous
- 8.2
- convergence of geometric sequence
- 7.6
- convergence of geometric series
- 7.6
- convergence of search sequence
- 5.1
- convergence, absolute
- 11.4
- convergence, circle of
- 12.2
- convergence, disc of
- 12.2
- convergence, radius of
- 12.2
- convergence
- 7.2
- convergent sequence, limit of
- 7.5
- convergent sequence, product theorem
- 7.5
- convergent sequence, reciprocal theorem
- 7.5
- convergent sequence, sum theorem
- 7.5
- convergent sequence, uniqueness theorem
- 7.5
- convergent sequence
- 7.2
- convergent sequences, quotient theorem
- 7.5
- convergent sequences
- 7.5
- copy (of
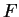 in
in 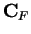 )
) - 4.1
- cosine, complex
- 11.4
- cosine
- 12.3 | 12.7
- critical point theorem
- 10.2
- critical point
- 10.2
- D
- D'Alembert, Jean (1717-1783)
- 11.4
- De Moivre's formula
- 6.2
- De Moivre, Abraham (1667-1754)
- 6.5
- decimal notation
- 7.6
- decimals
- intro
- decomposition theorem
- 7.5
- decreasing function
- 5.3
- decreasing sequence
- 7.8
- definition by recursion
- 3.3
- derivative
- 10.1
- Descartes, Rene, 1596-1650
- 3.5
- Dickson, Leonard Eugene, (1874-1954
- 2.3
- difference of sets
- 1.4
- difference, symmetric
- 2.1
- differential equation
- 12.4
- differentiation of power series
- 12.3
| 12.8
- digits
- 2.4
- direction in
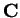
- 6.3
- direction of complex number
- 6.3
- disc of convergence
- 12.2
- disc open
- 6.2
- disc, closed
- 6.2
- disc, unit
- 6.2
- distance (in ordered field)
- 2.7
- distributive law in
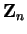
- B.
- distributive law in a field
- 2.5
- distributive law
- 2.3
- distributive
- 2.2
- divergence of search sequence
- 5.1
- divergence test
- 7.7
- divergent sequence
- 7.2
- division in a field
- 2.5
- domain of function
- 1.5
- double inverse theorem
- 2.1 | 2.4
- draughts
- 3.2
- dull sequence
- 7.3
- E
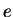
- 12.4
| 12.9
- empty set
- 1.1
- endpoints of an interval
- 2.7
- entertainments
- intro
- Epicureans
- 6.2
- equality of functions
- 1.5
- equality of objects
- 1.3
- equality of ordered pairs
- 1.4
- equality of rules
- 1.5
- equality of sets
- 1.1
- equality, reflexive property
- 1.3
- equality, substition property
- 1.3
- equality, symmetric property
- 1.3
- equality, transitive property
- 1.3
- equivalence for sets of propositions
- 2.5
- equivalence of propositions
- 1.2
- Euclid (365-300BC??)
- 3.1
| 3.2 | 3.2 | 5.3 | 6.2
- Euler, Leonard (1707-1783)
- 4.2
| 6.5
| 11.2 | 12.9
- Euler, summation notation
- 3.5
- even integer
- 3.2
- even number
- 3.1
- exercises
- intro
- exponential function
- 12.4
- exponents, laws for fractional
- 5.3
- exponents, rational
- 5.3
- extreme value theorem
- 9.1
- F
- factorial function
- 3.3
- factorial
- 3.5
- factorization of
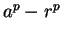
- 3.4
- factorization (depends on field)
- 3.4
- feature
- 2.2
- field, axioms for
- 2.3
- field, orderable
- 2.6
- field, real
- 5.2
- function, complex
- 8.1
- function, increasing and decreasing
- 5.3
- function, recursive
- 3.3
- function
- 1.5
- functions, addition and multiplication of
- 5.3
- G
- Göttingen
- 11.4
- Gauss, Carl (1777-1855)
- 12.7
- geometric sequence, convergence of
- 7.6
- geometric sequence
- 7.1 | 11.1
- geometric series, convergence of
- 7.6
- geometric series
- 3.4
- geometric series
- 7.1 | 11.1
- graph
- 5.3
- Gregory, John (1638-1675)
- 11.4
| 12.9
- H
- Hamilton, William R. (1805-1865)
- 2.2
| 4.2
- harmonic series
- 11.1 | 11.4
- Huntington, Edward (1874-1952)
- 2.5
| 2.7
- hyperbolic functions
- 12.6
- I
- identity element for binary operation
- 2.1
- image of a function
- 6.5
- imaginary axis
- 6.2
- imaginary part of complex number
- 6.1
- implication
- 1.2
- incommensurables
- 3.2 | 3.2
- increasing function
- 5.3
- increasing sequence
- 7.8
- induction theorem (generalized)
- 3.1
- induction theorem
- 3.1
- inductive
- 3.1
- inequalities, addition of
- 2.6
- inequalities, multiplication of
- 2.6
- inequality theorem
- 7.7
- inequality, triangle
- 2.7
- infinite series
- 11.1
- integer, even
- 3.2
- integer, odd
- 3.2
- integers in a field
- 3.2
- integers, informal definition
- 1.1
- integers
- 3.2
- interior point
- 10.2
- interior
- 10.2
- intermediate value theorem
- 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.2
- intersection
- 1.4
- interval, closed or open
- 5.1
- interval
- 2.7
- inverse for binary operation
- 2.1
- inverse of cat
- 6.5
- invertible element for binary operation
- 2.1
- J
- Jones, William, (1675-1749)
- 12.9
- K
- Koch, Helge von (1870-1924)
- 7.8
- Kramp, Christian, 1760-1826
- 3.5
- L
- Lagrange, Joseph, (1736-1813)
- 11.4
- Landau, Edmund (1877-1938)
- 11.4
- The Laws
- 3.2
- laws of exponents (fractional)
- 5.3
- laws of signs
- 2.6
- Laws of Thought
- 2.2
- least element principle
- 3.1
- Leibniz, Gottfried (1646-1716)
- 11.4
| 11.4 | 12.9
- length of complex number
- 6.3
- limit comparison test
- 11.2
- limit of a function
- 8.3
- limit of sequence
- 7.5
- limit point
- 8.3
- limit, uniqueness of
- 8.3
- line segment
- 10.2
- logarithm
- 12.5
- lower bound for a set
- 9.1
- lower bound for sequence
- 7.8
- M
- Madhava of Sangamagramma (c. 1340-1425)
- 10.3
| 11.4
| 12.9
- Mahavira (ninth century)
- 3.1
- Maple
- 2.2 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 4.2
| 12.6 | 12.9 | 12.9
- maps to
- 7.1
- Mathematica
- 3.5 | 3.5 | 4.2
| 12.6 | 12.9 | 12.9
- maximizing set
- 9.1
- maximum function
- 3.5 | 3.5
- maximum, critical point theorem
- 10.2
- maximum
- 9.1
- mean value theorem
- 10.2
- Mercator, Nicolaus(1620-1687)
- 11.4
- midpoint
- 5.1
- minimum
- 9.1
- monotonic sequence
- 7.8
- multiplication (field operation)
- 2.3
- multiplication in
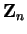
- 2.2
- multiplication of inequalities
- 2.6
- multiplication table
- 2.2
- Mycielski, Jan
- 7.8
- N
- natural numbers, informal definition
- 1.1
- natural numbers
- 3.1 | 3.2
- negative elements in ordered field
- 2.6
- Newton, Isaac (1643-1727)
- 5.3
| 10.3
| 11.4
- not, negation
- 1.2
- null sequence, comparision theorem
- 7.3
- null sequence, root theorem
- 7.3
- null sequence, sum theorem
- 7.4
- null sequence
- 7.3
- null sequences, product theorem
- 7.4
- null-times-bounded theorem
- 7.5
- number, odd
- 3.1
- number, even
- 3.1
- numbers natural
- 3.2
- numbers, complex
- 6.1
- numbers, natural
- 3.1
- numbers, rational
- 3.2
- numbers, real
- 5.2
- O
- odd integer
- 3.2
- odd number
- 3.1
- open interval
- 5.1
- opposite sign
- 2.6
- or, logical connective
- 1.2
- orderable field
- 2.6
- ordered field, axioms for
- 2.6
- ordered field, completemess of
- 5.2
- ordered pair
- 1.4
- ordered triple
- 1.4
- Oresme, Nicole (1323-1382)
- 11.4
- P
- pair, ordered
- 1.4
- paradox
- 1.6
- parentheses
- 2.3
- Pascal, Blaise (1623-1662)
- 3.1
- path
- 10.2
- Peano,Giuseppe (1858-1932)
- 3.1
- periodicity of
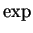
- 12.6
- periodicity of
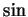 and
and
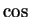 ,
,
- 12.59A h) and i)
| 12.6
- Philitas of Cos
- 1.6
- pi
-
- 12.6
| 12.9
- Plato (427?-347B.C.), The Laws
- 3.2
- polar decomposition
- 6.3
- polygon representation for a complex sequence
- 7.1
- polygon, snowflake
- 7.6
- positive elements in ordered field
- 2.6
- power function
- 3.3 | 3.5
- power rule for differentiation
- 10.1
- power series
- 12.1
- power, integer
- 3.3
- precedence
- 2.3
- precision function
- 7.3 | 7.8
- Priora Analytica
- 3.2
- Proclus
- 6.2
- product formula for absolute value
- 2.7
- product of functions
- 5.3
- product rule for differentiation
- 10.1
- product theorem for null sequences
- 7.4
- product theorem for continuous functions
- 8.2
- product theorem for convergent sequences
- 7.5
- product theorem for limits of functions
- 8.3
- proposition form
- 1.4
- proposition
- 1.2
- propositions, equivalence of
- 1.2
- Pythagorean theorem
- 6.2
- Q
- quadratic formula
- 2.5
- quotient formula for absolute value
- 2.7
- quotient rule for differentiation
- 10.1
- quotient theorem for continuous functions
- 8.2
- quotient theorem for convergent sequences
- 7.5
- quotient, of functions
- 5.3
- R
- radius of convergence
- 12.2
- ratio for a geometric sequence
- 7.1
- ratio for geometric series
- 7.1
- ratio test
- 11.2 | 11.4
- rational exponents
- 5.3
- rational numbers in a field
- 3.2
- rational numbers, informally defined
- 1.1
- rational numbers
- 3.2
- rational, (in sense of Euclid)
- 3.2
- real axis
- 6.2
- real field
- 5.2
- real part of comlex number
- 6.1
- reciprocal rule for differentiation
- 10.1
- reciprocal theorem for convergent sequences
- 7.5
- recursion
- 3.3
- Reed College
- intro
- restriction theorem
- 10.2
- reverse triangle inequality
- 7.5
- Rolle's theorem
- 10.2
- Rolle, Michel (1672-1719)
- 10.3
- root of complex number
- 6.3
- root of real number (theorem 5.49)
- 5.3
- root theorem for null sequences
- 7.3
- roots of complex numbers
- 12.6
- roots, continuity of
- 8.2
- rule, recursive
- 3.3
- Russell's paradox
- 1.6
- Russell, Bertrand 1872-1970
- 1.6
- S
- Sangamagramma, Madhava (c. 1340-1425)
- 10.3
- Schreier, Otto (1901-1929)
- 2.7
- search sequence, convergence of
- 5.1
- search sequence
- 5.1
- segment
- 10.2
- sequence, bounded
- 7.5
| 7.5
- sequence, constant
- 7.1 | 7.2
- sequence, convergent
- 7.2 | 7.2 | 7.5
- sequence, decreasing
- 7.8
- sequence, divergent
- 7.2
- sequence, dull
- 7.3
- sequence, increasing
- 7.8
- sequence, lower bound
- 7.8
- sequence, null
- 7.3
- sequence, search
- 5.1
- sequence, summable
- 11.1
- sequence, upper bound
- 7.8
- sequence
- 5.1
| 7.1
- series alternating
- 11.3
- series operator
- 11.1
- series, power series
- 12.1
- series, sum of
- 11.1
- series
- 11.1
- Servois, Francois-Joseph (1767-1847)
- 2.2
- set
- 1.1
- set difference
- 1.4
- set empty
- 1.1
- sine, complex
- 11.4
- sine
- 12.3 | 12.7
- Skolem functions
- 7.8
- snowflake
- 7.6 | 7.8
- square
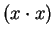
- 2.5
- square root of complex number
- 6.4
- square root
- 2.6
- subset
- 1.1
| 1.1
- substition property of equality
- 1.3
- subtraction in a field
- 2.5
- sum of a series
- 11.1
- sum of functions
- 5.3
- sum theorem for continuous functions
- 8.2
- sum theorem for convergent sequences
- 7.5
- sum theorem for differentiable functions
- 10.1
- sum theorem for limits of fumctions
- 8.3
- sum theorem for null sequences
- 7.4
- sum theorem for series
- 11.1
- summable sequence
- 11.1
- summable, absolutely
- 11.4
- summation function
- 3.5
- summation
- 3.4
- symmetric difference
- 2.1
- T
- transitivity of
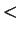
- 2.6
- transitivity of equality
- 1.3
- transitivity of implication
- 1.2
- translate of a sequence
- 7.7
- translation theorem
- 7.7
- triangle inequality , in
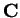
- 6.1
- triangle inequality, reverse
- 7.5
- triangle inequality
- 2.7 | 6.2
- trichotomy
- 2.6
- trigonometric functions
- 11.4 | 12.3 | 12.6 | 12.7
- triple, ordered
- 1.4
- U
- union
- 1.4
- uniqueness of
- 5.2
- uniqueness of identities
- 2.1
- uniqueness of inverses
- 2.1
- uniqueness of limits
- 8.3
- uniqueness theorem for convergent sequences
- 7.5
- unit circle
- 6.2
- unit disc
- 6.2
- upper bound for a set
- 9.1
- upper bound for sequence
- 7.8
- W
- Waring, Edward, (1734-1798)
- 11.4
- Weber, Heinrich Martin (1842-1913)
- 2.5
- Weierstrass, Karl (1815-1897)
- 2.7
| 9.2
- Z
- zero-one law
- 2.3


Next: About this document ...
Up: Numbers
Previous: B. Associativity and Distributivity