

Next: About this document ...
Up: Math 111 Calculus I
Previous: B. Proofs of Some
- A
- absolute value
- 3.3
| 6.1
- absolute value (derivative of)
- 11.1
- acceleration
- 15.2
- acceleration due to gravity
- 15.2
- addition law
- 9.1
| 9.1
- addition of points
- 4.1
- addition rule for area
- 5.2
- addition theorem for area
- B.
- additivity of area
- 5.1
- almost disjoint sets
- 5.2
- Analyst
- 10.1
- and (logical) operator
- 3.1
- antiderivative
- 12.4
| 17.1
- antiderivative theorem
- 12.4
- antidifferentiation, Maple commands
- 17.1
- Apollonius (c 260-170 B.C.)
- 10.1
- approachable point
- 10.2
- approximation
- 6.2
- approximation (strong approximation theorem)
- 6.2
- approximation to
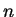 decimals
decimals
- 6.2
- arc length
- 9.1
- arccos
- 14.6
- arccot
- 14.6
- Archimedes(287-212 B.C.)
- 0.1
| 2.2
| 2.3
| 2.4
| 9.1
| 9.2
| 9.2
- Archimedes and
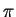
- 0.3
- Archimedes and
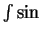
- 9.3
- Archimedes and
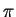
- 0.3
- Archimedes and area of parabolic segment
- 2.3
- arcsin
- 14.6
- arctan
- 14.6
- area = integral
- 8.6
- area as a number
- 1.
- area (assumptions about)
- 5.1
- area between graphs
- 8.6
- area function
- 5.1
| 5.2
- area of box
- 1.
- area of circle
- 8.5
- area of circular sector
- 17.5
- area of ellipse
- 8.5
- area of parabola
- 2.1
| 2.3
- area of parabolic segment
- 2.3
- area of snowflake
- 2.6
- area of triangle
- 5.3
- area under power function
- 7.2
- area, basic assumptions
- 5.1
- Aristotle(384-322 B.C.)
- 1.
| 10.1
| 10.3
- Aryabhata (circa 510)
- 9.1
- associative law for points
- 4.1
- assumptions about area
- 5.1
- assumptions: additivity of area
- 5.1
- assumptions: symmetry invariance of area
- 5.1
- assumptions: normalization of area
- 5.1
- assumptions: translation invariance of area
- 5.1
- average velocity
- 10.3
- B
- Babylonians
- 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.4
| 4.3
- Babylonians
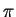
- 0.3
- Banach, Stefan(1892-1945)
- 5.1
- Berkeley, George (1685-1753)
- 10.1
- Bernoulli, Jacob (1654-1705)
- 2.2
| 6.3
| 6.7
- Bernoulli, Daniel(1700-1782)
- 14.6
- between,
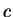 is between
is between 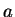 and
and 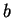 .
.
- 14.1
- bijective
- 14.3
- Bolzano, Bernard (1781-1848)
- 10.3
| 14.1
- bound for a function
- 5.1
- bounded function
- 5.1
- bounded set
- 5.1
- box
- 1.
- box (circumscribed)
- 2.1
- Brouncker, William(1620-1684)
- 5.5
- C
- Cantor, Georg (1845-1918)
- 1.
- Cartesian product.
- 3.2
- Cauchy, Augustin (1789-1857)
- 3.4
| 10.3
- Cavalieri, Bonaventura (1598-1647)
- 2.5
- chain rule
- 11.3
- change of scale for integrals
- 8.5
- chord of an arc
- 9.1
- circle (area of)
- 8.5
- circle (definition of)
- 4.3
- circle (unit)
- 4.3
- circular sector (area of)
- 17.5
- circumscribed box
- 2.1
- circumscribed hexagon for snowflake
- 2.6
- clockwise
- 9.1
- closed interval
- 1.
- codomain
- 3.3
- commutative law for points
- 4.1
- composition of continuous functions
- 12.1
- composition of functions
- 11.3
- composition problem
- 11.3
- compound interest
- 6.7
- computer calculation of area
- 5.6
- congruence problem
- 5.1
- conic section
- 10.1
- conservation of energy
- 15.2
- constant sequence
- 6.4
- constructivists
- 3.1
- continuity defined
- 12.1
- continuity on a set
- 12.1
- contrapositive
- 3.1
- convergent sequence
- 6.3
| 6.3
- convex downward (spills water)
- 15.3
- convex upward (holds water)
- 15.3
- cosh
- 14.6
- cosine defined
- 9.1
- cosine, integral of
- 9.3
| 9.3
- cot
- 11.2
- counterclockwise
- 9.1
- critical point
- 12.3
- critical point theorem I
- 12.3
- critical point theorem II
- 12.3
- critical set
- 12.3
- csc
- 11.2
- D
- decreasing function
- 5.3
- derivative
- 0.1
| 0.1
- derivative defined
- 10.3
- derivative (fractional)
- 15.1
- derivative (higher order)
- 15.1
- derivative of absolute value
- 11.1
- derivative of
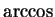
- 14.6
- derivative of arccot
- 14.6
- derivative of
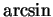
- 14.6
- derivative of
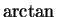
- 14.6
- derivative of
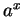
- 14.6
- derivative of
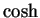
- 14.6
- derivative of exponential
- 14.6
- derivative of logarithm
- 11.1
- derivative of order 0
- 15.1
- derivative of powers
- 11.1
- derivative of reciprocal
- 11.2
- derivative of
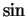 and
and 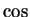
- 11.1
- derivative of
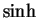
- 14.6
- derivative of trigonometric functions
- 11.2
- derivative of
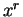
- 14.6
- derivative (second)
- 15.1
- derived function
- 0.1
- Descartes, Rene (1596-1660)
- 10.1
- difference of sets
- 1.
- differential
- 0.1
| 0.1
| 11.1
- differentiation
- 0.1
- differentiation, logarithmic
- 11.3
- Dirichlet,P.G.Lejenue(1805-1859)
- 8.3
- discontinuous function
- 12.1
- disjoint sets
- 5.1
- disjoint (almost disjoint sets)
- 5.2
- distance between numbers
- 6.1
- distance between points
- 4.3
- distributive law for points
- 4.1
- divergent sequence
- 6.3
- domain
- 3.3
- double angle formulas
- 9.1
- dummy index
- 1.
- dummy variable
- 3.4
| 8.2
| 10.2
- E
- e
- 5.4
- e (numerical calculatioin of)
- 6.7
- ellipse (area of)
- 8.5
- Emperor Yu(c. 21st century B.C.)
- 4.3
- end points of interval
- 1.
- entertainment
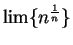
- 6.7
- entertainment
(Calculation of sines)
- 9.1
- entertainment
(Discontinuous derivative problem)
- 15.3
- entertainment
(Falling bodies problem)
- 10.1
- entertainment (Archimedes sine integral)
- 9.3
- entertainment (Calculate
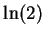 )
)
- 5.4
- entertainment (Composition problem)
- 11.3
- entertainment (Area of a triangle)
- 5.3
- entertainment (Square root problem)
- 0.3
- entertainment (Calculate
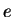 )
)
- 5.4
- entertainment (Pine Tree problem)
- 2.4
- entertainment (Snowflake problem)
- 2.6
- entertainment (Bernoulli's problem)
- 2.2
- entertainment (Calculation of
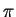 )
)
- 0.3
- entertainment (Congruence problem)
- 5.1
- equal functions
- 3.3
- equal propositions
- 3.1
- equivalent proposition
- 3.1
- error function
- 17.1
- etymology of corollary
- 5.2
- etymology of sine
- 9.1
- Euclid ( fl. c. 300 B.C.)
- 1.
| 2.4
| 10.1
| 10.3
- Euler, Leonard (1707-1783)
- 3.3
| 6.3
- Euler (summation notation)
- 3.4
- even function
- 12.4
- exponential function
- 14.3
| 14.4
- exponential function (derivative of)
- 14.6
- exponential function (properties of)
- 14.4
- extreme point
- 12.3
- extreme point (local)
- 12.3
- extreme value property
- 12.3
- F
- fluxion
- 0.1
| 11.1
- Fourier, Joseph (1768-1830)
- 8.1
| 15.1
- fractional derivatives
- 15.1
- function
- 0.1
- function (bounded)
- 5.1
- function (defined)
- 3.3
- function (Euler's definition)
- 3.3
- function (increasing)
- 5.3
- functions equal
- 3.3
- functions (operations on)
- 8.2
- fundamental theorem of the calculus
- 0.1
- fundamental theorem of calculus I
- 16.
- fundamental theorem of calculus II
- 16.
- Fundamental theorem of calculus (Leibniz statement of)
- 16.
- G
- Galileo (1564-1642)
- 10.1
| 10.1
- geometric series
- 6.6
- geometric series (finite)
- 2.4
- Gougu
- 4.3
- graph
- 3.3
- graphs (area between)
- 8.6
- gravity (acceleration due to)
- 15.2
- H
- half angle formulas
- 9.1
- Hausdorff, Felix (1868-1942)
- 5.1
- height of box
- 1.
- Heine, Heinrich Eduard (1821-1881)
- 10.3
- Heron (sometime between 250B.C and 150 A.D.)
- 13.3
- higher order derivatives
- 15.1
- hyperbolic functions
- 14.6
- I
- Ibn-al-Haitham (circa 1000 A.D.)
- 2.2
- image of
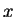 under
under 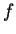
- 3.3
- image of
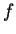
- 3.3
- implies
- 3.1
- increasing function
- 5.3
- indefinite integral
- 9.4
- induction
- 3.5
- inequality rule for limits of functions
- 10.2
- inequality rule for sequences
- 6.4
- inequality theorem for integrals
- 8.2
- inflection point
- 15.3
- injective
- 14.3
- inner snowflake
- 2.6
- instantaneous velocity
- 10.3
- integrable function
- 8.1
- integral
- 8.1
- integral (as area under a curve)
- 8.6
- integral (Ei = exponential integral)
- 17.1
- integral indefinite
- 9.4
- integral of
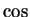
- 9.3
| 9.3
- integral of
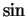
-
9.3
| 9.3
- integral (Si = sine integral)
- 17.1
- integral (change of scale in)
- 8.5
- integration
- 0.1
- integration by parts
- 17.3
- integration by substitution
- 17.4
- integration of rational functions
- 17.7
- interior point
- 10.2
- intermediate value property
- 14.1
| 14.1
| 14.1
- intersection of sets
- 1.
| 2.6
- interval
- 1.
- inverse function
- 14.3
- inverse function theorem
- 14.5
- K
- Katyayana (c. 600 BC or 500BC??)
- 4.3
- kinetic energy
- 15.2
- Koch, Helga von(1870-1924)
- 2.6
| 12.2
- L
- l'Hôpital,Guillaume François (1661-1701)
- 6.3
- Lagrange, Joseph Louis(1736-1813)
- 0.1
- 11.1
- Leibniz, Gottfried (1646-1716)
- 0.1
| 0.1
| 0.1
| 3.3
| 8.1
| 8.2
| 10.1
| 11.1
| 13.3
| 15.1
| 16.
- Leibniz (notation for sums)
- 3.4
- Leibniz (proof of product rule)
- 11.2
- length of arc
- 9.1
- limit of a sequence
- 6.3
- limit (one-sided)
- 13.1
- limits (infinite)
- 13.1
- lines
- 4.1
- Liouville, Joseph (1809-1882)
- 15.1
- ln(2) calculation
- 5.6
- ln(a)
- 0.1
- local maximum
- 12.3
- local minimum
- 12.3
- localization rule
- 11.1
- logarithm
- 5.4
| 5.4
| 7.2
- logarithm (derivative of)
- 11.1
- logarithmic differentiation
- 11.3
- M
- Maple
- 5.6
| 17.1
| 17.6
- Maple
leftsum
- 5.6
- Maple
rightsum
- 5.6
- Maple
average
- 5.6
- Maple calculation of
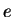
- 6.7
- Maple mypi
- 9.2
- Maple routine
- 9.2
- Maple sinsq
- 9.2
- Maple, approximate integration
- 5.6
- Maple, symbolic antidifferentiation
- 17.1
- Maple: integration
- 9.4
- maximum (local)
- 12.3
- maximum of function
- 12.3
- mean value theorem
- 12.4
- mean value theorem for integrals
- 16.
- Mercator, Nicolaus (1620-1687)
- 5.5
- mesh of partition
- 5.3
- minimum (local)
- 12.3
- minimum of function
- 12.3
- monotonic function
- 5.3
- monotonic (piecewise)
- 8.2
- monotonicity of area
- 5.2
| B.
- N
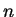 th root rule for sequences
th root rule for sequences
- 6.4
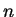 th power theorem
th power theorem
- 6.5
- Napier, John(1550-1632)
- 5.4
- Newton, Isaac(1642-1727)
- 0.1
| 0.1
| 10.3
| 11.1
- Newton's law (F=ma)
- 0.1
- nice function
- 16.
- non-integrable function
- 8.3
- normalization property of area
- 5.1
- not (logical) operator
- 3.1
- nowhere differentiable function
- 12.2
- Nullsequence rule
- 6.4
- number as area
- 1.
- O
- objects in a set
- 1.
- odd function
- 12.4
- open interval
- 1.
- operations on functions
- 8.2
- optical illusion
- 9.1
- optimization problems
- 13.2
- or (logical) operator
- 3.1
- ordered pair
- 3.2
- outer snowflake
- 2.6
- P
- pair (ordered pair)
- 3.2
- parabola (area of)
- 2.1
| 2.3
- parabolic segment (area of)
- 2.3
- parallelogram
- 4.1
- partition
- 5.3
- partition regular
- 5.3
- partition-sample sequence
- 8.2
- Pascal, Blaise (1623-1662)
- 2.2
- peicewise monotonic function
- 8.2
- piecewise monotonic (example of non-piecewise monotonic function)
- 12.2
- pi
- 0.1
| 0.3
| 0.3
| 5.6
| 8.5
- pi, computer calculation
- 5.6
- point in plane
- 1.
- point of inflection
- 15.3
- points (in
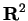 )
)
- 4.1
- points in a set
- 1.
- points (addition of)
- 4.1
- potential energy
- 15.2
- power function
- 14.4
- power (
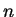 th power theorem)
th power theorem)
- 6.5
- power-sums (list of)
- 2.2
- prerequisites
- 0.2
- product rule for derivatives
- 11.2
- product rule for limits
- 10.2
- product rule for limits of functions
- 10.2
- product rule for sequences
- 6.4
- product (Cartesian)
- 3.2
- proofs without words
- 2.2
- proposition
- 3.1
- proposition (set defined by)
- 3.2
- proposition form
- 3.1
- propositions (equality of)
- 3.1
- propositions (equivalence of)
- 3.1
- Ptolemy, Claudius (fl 127-151)
- 9.1
- Pythagoras (f. 530-510 B.C.)
- 4.3
- Pythagoreans
- 2.2
- Q
- quadratic formula
- 4.3
- quotient rule for derivatives
- 11.2
- quotient rule for limits
- 10.2
- quotient rule for limits of functions
- 10.2
- quotient rule for sequences
- 6.4
- R
- Ramanujan, Srinivasa (1887-1920)
- 0.3
- rate of change
- 13.3
- rational functions
- 17.7
- rational number (definition)
- 1.
- real number
- 0.1
- reciprocal (derivative of)
- 11.2
- reflection
- 2.3
| 4.2
- reflection law for sin and cos
- 9.1
- reflection theorem
- 14.3
- regular partition
- 5.3
- Rhind Papyrus
- 0.3
- Riemann sum
- 7.1
- Riemann, Bernhard (1826-1866)
- 8.1
- right triangle
- 5.3
- rituals for integration
- 17.4
| 17.4
| 17.5
| 17.6
| 17.6
- Rolle, Michel (1652-1719)
- 12.4
- Rolle's theorem
- 12.4
- rotation
- 4.2
- ruler function
- 8.4
- S
- Saint-Vincent, Grégoire de, (1584-1667)
- 6.6
- sample
- 7.1
- Sarasa, Alfons Anton de (1618-1667)
- 5.4
- schizophrenia
- 3.1
- sec
- 11.2
- sector (circular)
- 17.5
- segment
- 4.2
- segments
- 4.1
- sequence
- 3.3
- sequence (constant sequence rule)
- 6.4
- sequence (convergent)
- 6.3
| 6.3
- sequence (divergent)
- 6.3
- sequence (null sequence rule)
- 6.4
- sequence (constant)
- 6.4
- sequence (limit of)
- 6.3
- sequence (product rule for)
- 6.4
- sequence (sum rule for)
- 6.4
- sequence (translate of)
- 6.4
- sequence (translation rule for)
- 6.4
- sequence (
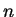 th root rule for)
th root rule for)
- 6.4
- sequences (inequality rule for)
- 6.4
- sequences (quotient rule for)
- 6.4
- set
- 1.
- set (bounded)
- 5.1
- sets defined by propositions
- 3.2
- sine (definition)
- 9.1
- sine (etymology of)
- 9.1
- sine (integral of)
- 9.3
| 9.3
- sine integral (Si)
- 17.1
- sinh
- 14.6
- snowflake
- 2.6
| 12.2
- snowflake (area of)
- 2.6
- spike function
- 8.2
| 8.2
| 10.2
- square root problem
- 0.3
- squeezing rule for limits of functions
- 10.2
- squeezing rule for sequences
- 6.4
- stretch
- 8.5
- Stringham, Irving
- 5.4
- subadditivity of area
- 5.2
- subinterval of a partition
- 5.3
- subset
- 1.
- substitution in integrals
- 17.6
- substitution (trigonometric)
- 17.5
- sum rule for derivatives
- 11.2
- sum rule for limits
- 10.2
- sum rule for limits of functions
- 10.2
- sum rule for sequences
- 6.4
- sum theorem for derivatives
- 17.2
- sum theorem for indefinite integrals
- 9.4
- sum theorem for integrals
- 8.2
- summation formula
- 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
| 2.2
- surjective
- 14.3
- symmetric set
- 12.4
- symmetry invariance
- 5.1
- symmetry of square
- 4.2
- T
- tangent
- 10.1
| 10.1
| 10.3
- tan
- 11.2
- translate of a sequence
- 6.4
- translate of set
- 4.2
- translation invariance
- 5.1
- translation rule for sequences
- 6.4
- triangle inequality
- 6.1
- triangle (area of)
- 5.3
- triangle (right)
- 5.3
- trick
- 6.5
- trigonometric functions (definition)
- 9.1
- trigonometric functions derivative of
- 11.1
| 11.2
- trigonometric identities
- 9.1
| 9.1
| 9.1
- trigonometric substitution
- 17.5
- U
- union of sets
- 1.
| 2.6
- uniqueness of inverses
- 14.3
- Uniqueness theorem for convergence
- 6.3
- unit circle
- 4.3
- V
- velocity
- 0.1
| 10.1
| 10.1
- velocity (average)
- 10.3
- velocity (instantaneous)
- 10.3
- W
- Weierstrass, Karl(1815-1897)
- 6.1
| 12.2
- width of box
- 1.
- work
- 0.1
- Z
- zero-area set
- 5.2
| 8.6
- zeroth order derivative
- 15.1
- Zu Chongzhi (429-500 A.D.)
- 0.3
Ray Mayer
2007-09-07