


Next: 4. Analytic Geometry
Up: 3. Propositions and Functions
Previous: 3.4 Summation Notation
Index
The induction principle is a way of formalizing the intuitive idea
that if you begin at 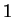 and start counting ``
and start counting ``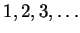 '', then
eventually you will reach any preassigned number (such as for example,
'', then
eventually you will reach any preassigned number (such as for example,
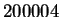 ).
).
3.55
Assumption (The Induction Principle)
Let
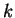
be an integer, and let
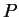
be
a proposition form over
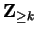
. If
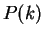 is true,
is true,
and
``for all
![$n \in \mbox{{\bf Z}}_{\geq k}[ P(n) \mbox{$\Longrightarrow$} P(n+1)]$](img804.gif) '' is true,
'' is true,
then
``for all
![$n \in \mbox{{\bf Z}}_{\geq k}[ P(n)]$](img805.gif) '' is true.
'' is true.
In order to prove ``for all
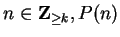 '' by using the induction
principle, you should
'' by using the induction
principle, you should
1. Prove that 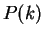 is true.
is true.
2. Take a generic element  of
of
 and
prove
and
prove
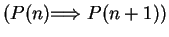 .
.
Recall that the way to prove ``
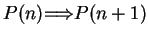 '' is true, is to
assume that
'' is true, is to
assume that 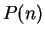 is true and show that then
is true and show that then 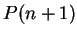 must be true.
must be true.
3.56
Example.
We will use the induction principle to do exercise
2.10. For all
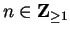
, let
Then
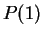
says
which is true, since both sides of this equation are equal to
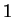
.
Now let
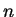
be a generic element of
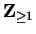
Then
It follows from the induction principle that
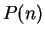
is true for all
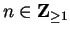
, which is what we wanted to prove.
3.57
Example.
We will show that
for all
![$n \in \mbox{{\bf Z}}_{\geq 4}[ n! > 2^n].$](img817.gif)
Proof: Define a proposition form 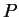 over
over
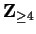 by
by
Now
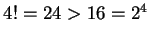 , so
, so 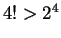 and thus
and thus 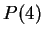 is true.
is true.
Let 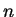 be a generic element of
be a generic element of
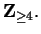 Since
Since
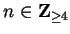 , we
know that
, we
know that
Hence
Hence, for all
![$n \in \mbox{{\bf Z}}_{\geq 4}[ P(n) \mbox{$\Longrightarrow$}P(n+1)].$](img830.gif) It follows from
the induction principle that for all
It follows from
the induction principle that for all
![$n \in \mbox{{\bf Z}}_{\geq 4}[ n! > 2^n].$](img817.gif)



Next: 4. Analytic Geometry
Up: 3. Propositions and Functions
Previous: 3.4 Summation Notation
Index
Ray Mayer
2007-09-07
![]() '' is true,
'' is true,
![]() '' is true.
'' is true.
![]() '' is true,
'' is true,
![]() '' is true.
'' is true.
![]() '' by using the induction
principle, you should
'' by using the induction
principle, you should
![]() is true.
is true.
![]() of
of
![]() and
prove
and
prove
![]() .
.
![]() '' is true, is to
assume that
'' is true, is to
assume that ![]() is true and show that then
is true and show that then ![]() must be true.
must be true.
![\begin{displaymath}P(n) = \left[\sum_{p=1}^n p^3 = \frac{n^2 (n+1)^2}{4}\right]. \end{displaymath}](img812.gif)
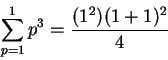
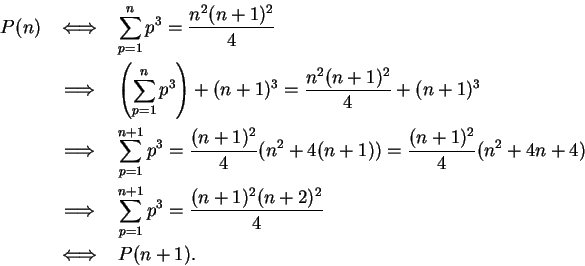
![]() over
over
![]() by
by
![]() , so
, so ![]() and thus
and thus ![]() is true.
is true.
![]() be a generic element of
be a generic element of
![]() Since
Since
![]() , we
know that
, we
know that ![]() It follows from
the induction principle that for all
It follows from
the induction principle that for all
![]()
![]()