

Next: 12.4 The Mean Value
Up: 12. Extreme Values of
Previous: 12.2 A Nowhere Differentiable
Index
12.10
Definition (Maximum, minimum, extreme points.)
Let
be a set, let
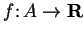
and let
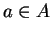
. We say that

has
a
maximum at
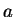
if
and we say that

has a
minimum at
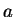
if
Points
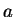
where

has a maximum or a minimum are called
extreme points
of 
.
12.11
Example.
Let
![$f\colon [0,1]\to\mbox{{\bf R}}$](img3164.gif)
be defined by
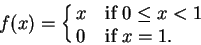 |
(12.12) |
Then

has a minimum at
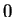
and at
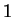
, but

has no maximum. To see that

has no maximum, observe that if
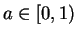
then
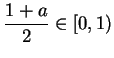
and
If
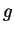
is the function whose graph is shown, then
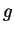
has a maximum at
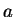
, and
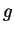
has minimums at
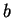
and
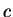
.
12.13
Assumption (Extreme value property.)
If

is a continuous function on the
interval
![$[a,b]$](img1071.gif)
, then

has a maximum and a minimum on
![$[a,b]$](img1071.gif)
.
The extreme value property is another assumption that is really a theorem,
(although the proof requires yet another assumption, namely completeness
of the real numbers.)
The following exercise shows that all of the hypotheses
of the extreme value property are necessary.
12.14
Exercise.
A
- a)
- Give an example of a continuous function
 on
on 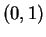 such that
such that
 has no maximum on
has no maximum on 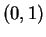 .
.
- b)
- Give an example of a bounded continuous function
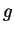 on
the closed interval
on
the closed interval 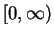 ,
such that
,
such that 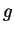 has no maximum on
has no maximum on 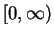
- c)
- Give an example of a function
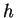 on
on ![$[0,1]$](img908.gif) such that
such that 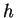 has
no maximum on
has
no maximum on ![$[0,1]$](img908.gif) .
.
- d)
- Give an example of a continuous function
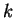 on
on
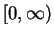 that has neither a maximum nor a minimum on
that has neither a maximum nor a minimum on 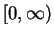 ,
or else explain why no such function exists.
,
or else explain why no such function exists.
12.15
Exercise.
A
- a)
- Show that every continuous function from an interval
![$[a,b]$](img1071.gif) to
to
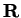 is bounded. (Hint: Use the extreme value property,)
is bounded. (Hint: Use the extreme value property,)
- b)
- Is it true that every continuous function from an open interval
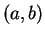 to
to
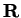 is bounded?
is bounded?
- c)
- Give an example of a function from
![$[0,1]$](img908.gif) to
to
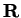 that is not
bounded.
that is not
bounded.
12.16
Definition (Critical point, critical set.)
Let

be a real valued function such that
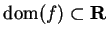
. A point
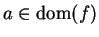
is called a
critical point for 
if
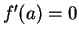
.
The set of critical points for

is the
critical set for

. The
points
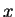
in the critical set for

correspond to points
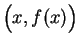
where the
graph of

has a horizontal tangent.
12.17
Theorem (Critical point theorem I.) Let  be a real valued function with
be a real valued function with
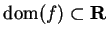 . Let
. Let
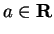 .
If
.
If  has a maximum (or a minimum) at
has a maximum (or a minimum) at 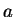 , and
, and  is differentiable at
is differentiable at 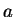 ,
then
,
then
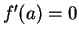 .
.
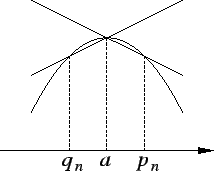
Proof: We will consider only the case where  has a maximum. Suppose
has a maximum. Suppose  has a
maximum at
has a
maximum at 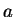 and
and  is differentiable at
is differentiable at 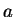 . Then
. Then 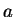 is an interior point
of
is an interior point
of
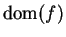 so we can find sequences
so we can find sequences 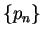 and
and 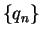 in
in
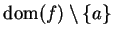 such that
such that 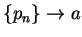 ,
, 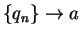 ,
, 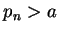 for all
for all
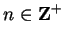 ,
and
,
and 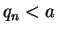 for all
for all
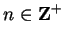 .
.
Since  has a maximum at
has a maximum at 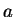 , we have
, we have
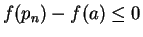 and
and
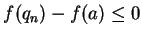 for all
for all 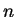 . Hence
. Hence
Hence by the inequality theorem for limits,
It follows that
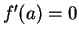 .
. 
12.18
Definition (Local maximum and minimum.)
Let

be a real valued function whose domain is a subset of
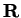
. Let
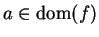
. We say that

has a
local maximum at
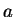
if there is a positive
number
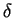
such that
and we say that

has a
local minimum at
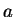
if there is a positive
number
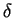
such that
Sometimes we say that

has a
global maximum at 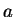
to mean that

has a
maximum at
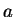
, when we want to emphasize that we do not mean local maximum.
If

has a local maximum or a local minimum at
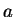
we say

has a
local extreme point at
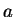
.
12.19
Theorem (Critical point theorem II.) Let  be a real valued function with
be a real valued function with
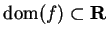 . Let
. Let
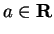 .
If
.
If  has a local maximum or minimum at
has a local maximum or minimum at 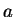 , and
, and  is differentiable at
is differentiable at 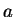 ,
then
,
then
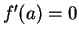 .
.
Proof: The proof is the same as the proof of theorem 12.17.
From the critical point theorem, it follows that to investigate the extreme
points
of  , we should look at critical points, or at points where
, we should look at critical points, or at points where  is not
differentiable (including endpoints of domain
is not
differentiable (including endpoints of domain  ).
).
12.21
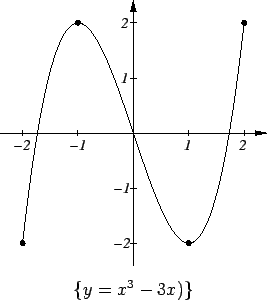
Example.
Let
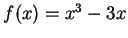
for
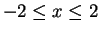
. Then

is differentiable everywhere
on
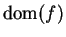
except at
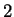
and
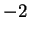
. Hence, any local extreme points are
critical
points of

or are in
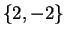
. Now
From this we see that the critical set for

is
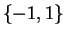
. Since

is a
continuous function on a closed interval
![$[-2,2]$](img3194.gif)
we know that

has a
maximum and a minimum on
![$[-2,2]$](img3194.gif)
. Now
Hence

has global maxima at
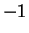
and
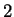
, and

has global minima at
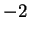
and
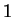
. The graph of

is shown.
12.22
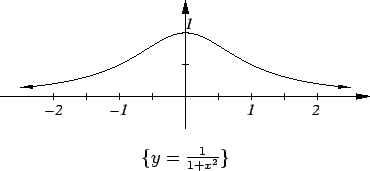
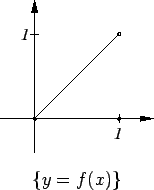
Example.
Let
Here
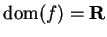
and clearly
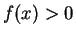
for all
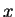
. I can see by inspection
that

has a maximum at
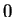
; i.e.,
I also see that
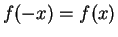
, and that

is strictly decreasing on
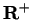
thus

has no local extreme points other than
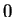
. Also
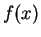
is very small when
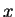
is large. There is no point in calculating the critical
points here because all the information about the extreme points is apparent
without the calculation.



Next: 12.4 The Mean Value
Up: 12. Extreme Values of
Previous: 12.2 A Nowhere Differentiable
Index
Ray Mayer
2007-09-07
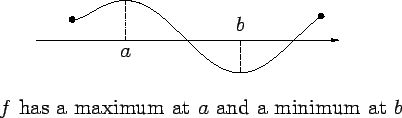
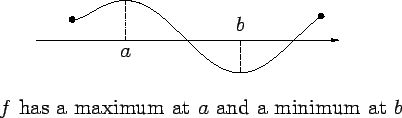
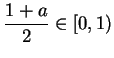 and
and
![]() has a maximum. Suppose
has a maximum. Suppose ![]() has a
maximum at
has a
maximum at ![]() and
and ![]() is differentiable at
is differentiable at ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() is an interior point
of
is an interior point
of
![]() so we can find sequences
so we can find sequences ![]() and
and ![]() in
in
![]() such that
such that ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() for all
for all
![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() for all
for all
![]() .
.
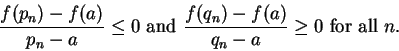
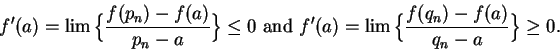
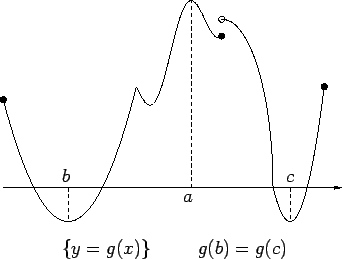
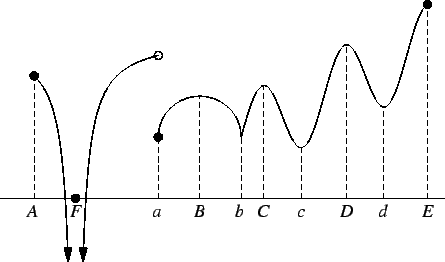
![]() whose graph is shown in the figure has local maxima at
whose graph is shown in the figure has local maxima at
![]() and local minima at
and local minima at ![]() , and
, and ![]() . It has a global maximum at
. It has a global maximum at ![]() , and it
has
no global minimum.
, and it
has
no global minimum.
![]() , we should look at critical points, or at points where
, we should look at critical points, or at points where ![]() is not
differentiable (including endpoints of domain
is not
differentiable (including endpoints of domain ![]() ).
).