


Next: 5.2 Completeness
Up: 5. Real Numbers
Previous: 5. Real Numbers
Index
5.1
Definition (Sequence.)
Let
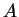
be a set. A
sequence in 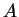
is a function
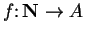
. I
sometimes denote the
sequence
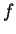
by
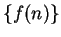
or
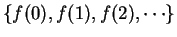
. For
example, if
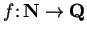
is defined by
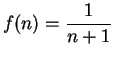
, I might write
5.2
Warning.
The notation
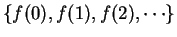
is always ambiguous.
For example,
might denote
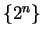
. It might also denote
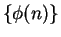
where
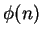
is the
number of regions into which a circle
is divided when all the segments joining the
vertices of an inscribed regular
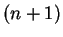
-gon are drawn.
5.3
Entertainment.
Show that
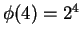
, but that it is not true that
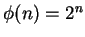
for all
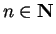
.
5.4
Warning.
The notation for a sequence and a set are the same, but a sequence is not a set. For
example, as sets,
But as sequences,
5.5
Notation (
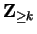 )
)
Recall from section
3.65, that If
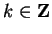
, then
Thus,
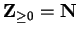
. Occasionally I will want to consider sequences whose
domain is
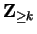
where
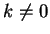
. I will denote such a sequence by
Hence, if
then
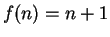
for all
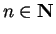
, and if
then
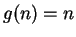
for all
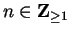
.
5.6
Remark.
Most of the results we prove for sequences
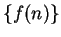
have obvious analogues for
sequences
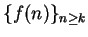
, and I will assume these analogues without
explanation.
5.7
Examples.

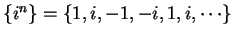
is a sequence in
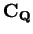
.
is a sequence of intervals in an ordered field
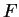
.
5.8
Definition (Open and closed intervals.)
An interval
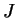
in an ordered field is
closed if it contains all of its
endpoints.
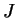
is
open if it contains none of its endpoints. Thus,
5.9
Definition (Binary search sequence.)
Let
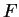
be an ordered field. A
binary search sequence ![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif)
in
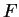
is a sequence of closed intervals with end points
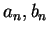
in
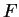
such that
- 1)
-
![$[a_{n+1},b_{n+1}]\subset [a_n,b_n]$](img1291.gif) for all
for all
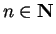 , and
, and
- 2)
-
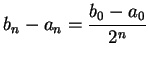 for all
for all
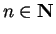 .
.
Condition 1) is equivalent to
5.10
Warning.
Note that the intervals in a binary search sequence are closed. This will be
important later.
5.11
Definition (Convergence of search sequence.)
Let
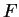
be an ordered field, let
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif)
be a binary search sequence in
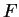
,
and let
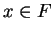
. We say
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif) converges
converges to
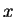
and
write
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}\to x$](img1294.gif)
if
![$x\in[a_n,b_n]$](img1295.gif)
for all
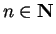
.
We say
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif) converges
converges, if there is some
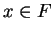
such that
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}\to x$](img1294.gif)
. We say
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif) diverges
diverges if there is no such
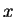
.
5.12
Example.
Let
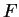
be an ordered field. Then
![$\displaystyle { \left\{\left[0,{1\over
{2^n}}\right]\right\}}$](img1296.gif)
is a binary search sequence and
![$\displaystyle {\left\{\left[0,{1\over
{2^n}}\right]\right\}\to 0}$](img1297.gif)
.
5.13
Exercise.
Let
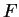
be an ordered field, let
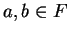
with
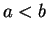
. Let
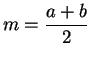
. Show that
- 1)
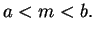
- 2)
-
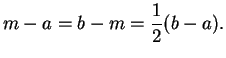
(Conditions 1) and 2) say that
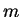
is the midpoint
of
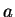
and
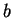
.)
5.14
Exercise.
Let
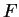
be an ordered field and let
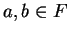
with
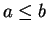
and let
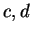
be
points in
![$[a,b]$](img1303.gif)
. Show that
i.e., if two points lie in an interval then the distance between the points is less
than or equal to the length of the interval.
5.15
Exercise.
A
Show that
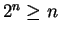
for all
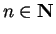
.
5.16
Example (A divergent binary search sequence.)
Define a binary search
sequence
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif)
in
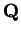
by the rules
Thus,
Since
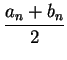 is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![$[a_n,b_n]$](img1311.gif) , we have
, we have
and
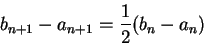 |
(5.17) |
It follows from (5.17) that
Hence ![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif) is a binary search sequence. For each
is a binary search sequence. For each
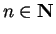 , let
, let 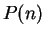 be
the proposition
be
the proposition
Then 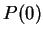 says
says 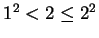 , so
, so 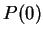 is true. Let
is true. Let
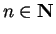 .
If
.
If
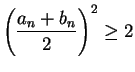 , then
, then
If
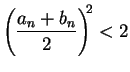 , then
, then
Hence, in all cases,
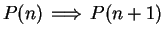 , and by induction,
, and by induction,
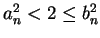 for
all
for
all
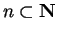 . Since
. Since 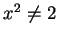 for all
for all
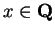 , we have
, we have
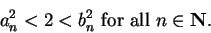 |
(5.18) |
I now will show that ![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}$](img1289.gif) diverges. Suppose, in order to
get a contradiction, that for some
diverges. Suppose, in order to
get a contradiction, that for some
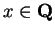 ,
,
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}\to x$](img1294.gif) . Then
. Then
so
Combining this with (5.18), we get
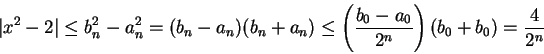 |
(5.19) |
for all
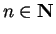 . Since
. Since 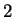 is not a square in
is not a square in
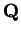 ,
, 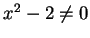 . Write
. Write
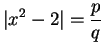 , where
, where
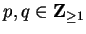 . Then
. Then
so
By exercise 5.15A, for all
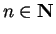 ,
,
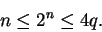 |
(5.20) |
Statement (5.20) is false when 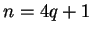 , and hence our assumption that
, and hence our assumption that
![$\{[a_n,b_n]\}\to x$](img1294.gif) was false.
was false.



Next: 5.2 Completeness
Up: 5. Real Numbers
Previous: 5. Real Numbers
Index
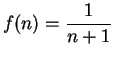 , I might write
, I might write
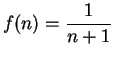 , I might write
, I might write
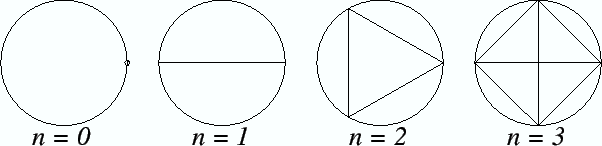
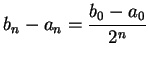 for all
for all
![$\displaystyle { \left\{\left[0,{1\over
{2^n}}\right]\right\}}$](img1296.gif) is a binary search sequence and
is a binary search sequence and
![$\displaystyle {\left\{\left[0,{1\over
{2^n}}\right]\right\}\to 0}$](img1297.gif) .
.
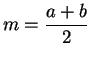 . Show that
. Show that
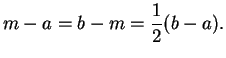
![\begin{displaymath}{{a_0+b_0}\over 2}={{1+2}\over 2}={3\over 2}; \hspace{.2in}\l...
...>2, \mbox{ so }[a_1,b_1] = \left[ {2\over 2},{3\over 2}\right];\end{displaymath}](img1307.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}{{a_1+b_1}\over 2}={{ {2\over 2}+{3\over 2}}\over 2} ={5\over...
...}<2, \mbox{ so } [a_2,b_2]=\left[ {5\over
4},{6\over 4}\right];\end{displaymath}](img1308.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}{{a_2+b_2}\over 2}={{ {5\over 4}+{6\over 4}}\over 2}={{11}\ov...
...mbox{ so } [a_3,b_3]=\left[
{{11}\over 8},{{12}\over 8}\right].\end{displaymath}](img1309.gif)
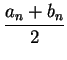 is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of 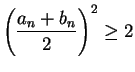 , then
, then
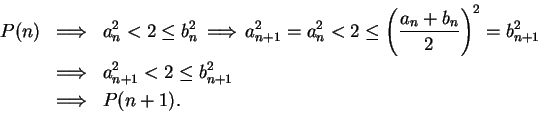
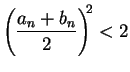 , then
, then
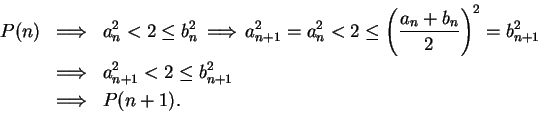
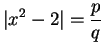 , where
, where