


Next: 7.8 Bounded Monotonic Sequences
Up: 7. Complex Sequences
Previous: 7.6 Geometric Series
Index
7.7 The Translation Theorem
7.73
Theorem.
Let 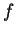 be a real convergent sequence, say
be a real convergent sequence, say 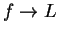 .
If
.
If 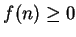 for all
for all
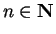 , then
, then 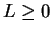 .
.
Proof: I note that
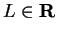 , since if
, since if 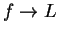 , then
, then
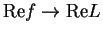 . Suppose,
to get a contradiction, that
. Suppose,
to get a contradiction, that 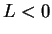 , (so
, (so
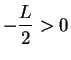 ), and let
), and let
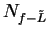 be a precision function for the null sequence
be a precision function for the null sequence 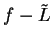 .
Let
.
Let
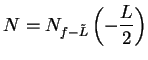 . Then
. Then
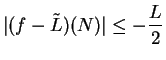 , so
, so
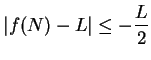 , and hence
, and hence
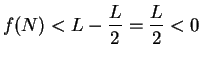 .
This contradicts the assumption that
.
This contradicts the assumption that  for all
for all
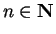 .
.
7.74
Exercise (Inequality theorem.)
A
Let
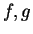
be convergent real sequences. Suppose that
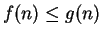
for all
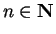
. Prove that
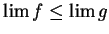
.
7.75
Exercise.
A
Prove the following assertion, or
give an example to show that
it is not true. Let
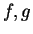
be convergent real sequences. Suppose that

for all
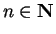
. Then
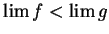
.
7.76
Definition (Translate of a sequence.)
Let
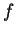
be a sequence and let
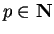
. Then the sequence
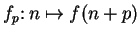
is called a
translate of 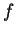
.
7.77
Example.
If
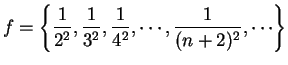
, then
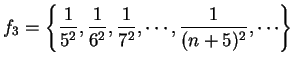
. A translate of a
sequence is a sequence obtained by ignoring the first few terms.
7.78
Theorem (Translation theorem.)
If 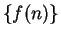 is a convergent complex sequence, and
is a convergent complex sequence, and
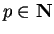 , then
, then  converges, and
converges, and
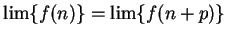 . Conversely, if
. Conversely, if  converges,
then
converges,
then 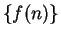 converges to the same limit.
converges to the same limit.
Proof: Let 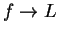 , let
, let 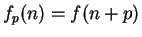 and let
and let
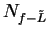 be a precision
function for
be a precision
function for 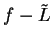 . I claim
. I claim
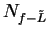 is also a precision function for
is also a precision function for
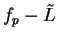 . In fact, for all
. In fact, for all
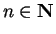 , and all
, and all
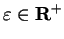 ,
,
Conversely, suppose
and let
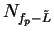 be a precision function for
be a precision function for 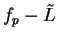 . Let
. Let
 for all
for all
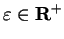 . I
claim
. I
claim 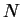 is a precision function for
is a precision function for
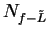 . For all
. For all
 ,
,
7.79
Example.
Let the sequence
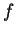
be defined by
Then
Suppose I knew that
converged to a limit
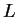
. It is clear that
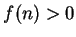
for all
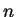
, so
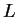
must be

. By the translation theorem
so

; i.e.,
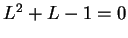
. Hence
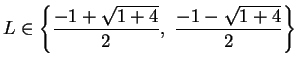
, and since
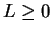
, we conclude
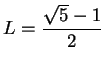
. I've shown that the only thing that
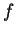
can possibly converge to is
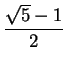
. Now
Since
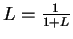
, we have for all
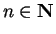
,
Hence
and by induction,
By theorem
7.64 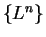
is a null sequence, and by the
comparison theorem for null sequences, it follows that
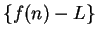
is a null sequence. This completes the proof
that
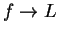
.
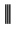
7.80
Exercise.
Let
- a)
- Assume that
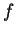 converges, and determine the value of
converges, and determine the value of 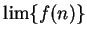 .
.
- b)
- Calculate
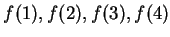 , using all of the accuracy of your
calculator. Does the sequence appear to converge?
, using all of the accuracy of your
calculator. Does the sequence appear to converge?
7.81
Entertainment.
Show that the sequence
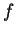
defined in the
previous exercise converges. We will prove this result in Example
7.97,
but you can prove it now, using results you know.
7.82
Exercise.
Let
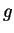
be the sequence defined by
- a)
- Assume that
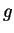 converges, and determine the value of
converges, and determine the value of 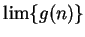 .
.
- b)
- Calculate
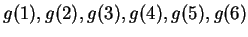 , using all of the accuracy of your
calculator. Does this sequence converge?
, using all of the accuracy of your
calculator. Does this sequence converge?
7.83
Theorem (Divergence test.)
Let 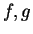 be complex sequences such that
be complex sequences such that 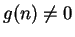 for all
for all
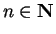 . Suppose that
. Suppose that 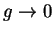 and
and 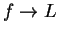 where
where 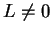 . Then
. Then
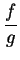 diverges.
diverges.
Proof: Suppose, to get a contradiction, that
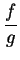 converges to a limit
converges to a limit
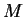 . Then by the product theorem,
. Then by the product theorem,
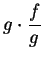 converges to
converges to 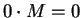 ;
i.e.,
;
i.e., 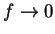 . This contradicts our assumption that
. This contradicts our assumption that 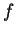 has a non-zero limit.
has a non-zero limit.
7.84
Exercise.
Prove the following assertion or give an example to show that it is not true:
Let
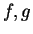
be complex sequences such that
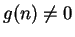
for all
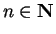
, but
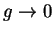
. Then
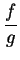
diverges.
7.85
Example.
Let
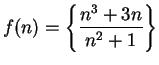
for all
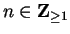
.
Then
Since
and
it follows that
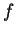
diverges.
7.86
Exercise.
A
Let
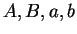
be complex numbers
such that
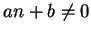
for all
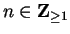
. Discuss the convergence of
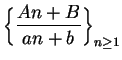
. Consider all possible choices for
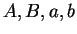
.



Next: 7.8 Bounded Monotonic Sequences
Up: 7. Complex Sequences
Previous: 7.6 Geometric Series
Index
![]() , since if
, since if ![]() , then
, then
![]() . Suppose,
to get a contradiction, that
. Suppose,
to get a contradiction, that ![]() , (so
, (so
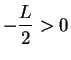 ), and let
), and let
![]() be a precision function for the null sequence
be a precision function for the null sequence ![]() .
Let
.
Let
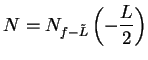 . Then
. Then
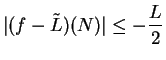 , so
, so
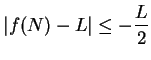 , and hence
, and hence
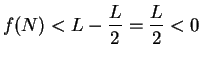 .
This contradicts the assumption that
.
This contradicts the assumption that ![]() for all
for all
![]() .
.
![]()
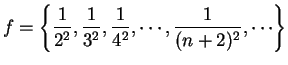 , then
, then
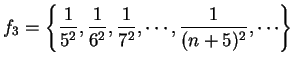 . A translate of a
sequence is a sequence obtained by ignoring the first few terms.
. A translate of a
sequence is a sequence obtained by ignoring the first few terms.
![]() , let
, let ![]() and let
and let
![]() be a precision
function for
be a precision
function for ![]() . I claim
. I claim
![]() is also a precision function for
is also a precision function for
![]() . In fact, for all
. In fact, for all
![]() , and all
, and all
![]() ,
,
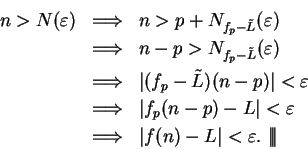

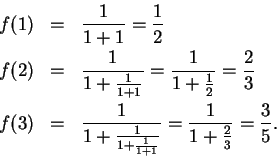
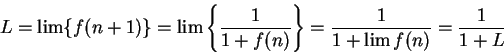
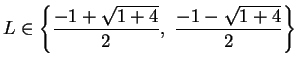 , and since
, and since 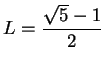 . I've shown that the only thing that
. I've shown that the only thing that 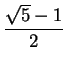 . Now
. Now
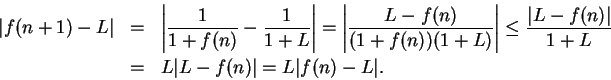

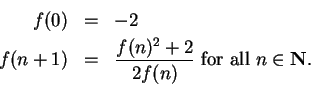
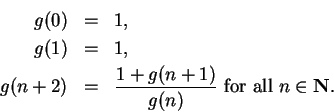
![]() converges to a limit
converges to a limit
![]() . Then by the product theorem,
. Then by the product theorem,
![]() converges to
converges to ![]() ;
i.e.,
;
i.e., ![]() . This contradicts our assumption that
. This contradicts our assumption that ![]() has a non-zero limit.
has a non-zero limit.
![]()
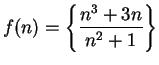 for all
for all
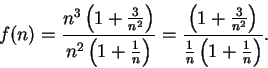
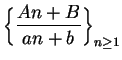 . Consider all possible choices for
. Consider all possible choices for