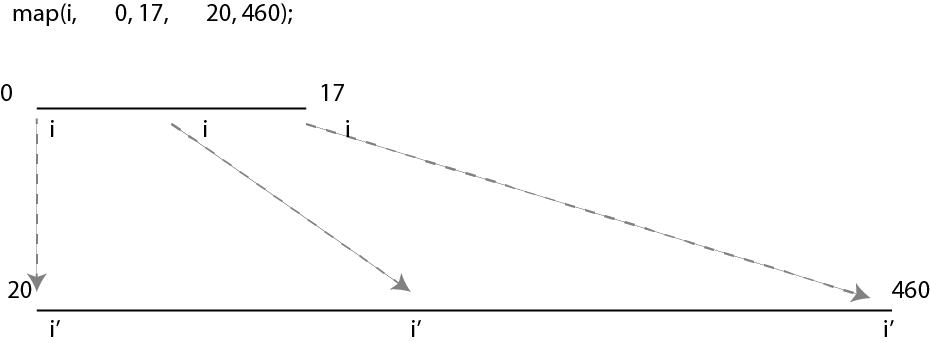
map() - Linear Movement
- map function maps a range of numbers (0 to 17) to another range (20 to 460) in the below example.

void setup() {
size(400, 200);
noStroke();
}
void draw() {
background(204);
// map range (0-width) to (30-370)
float x2 = map(mouseX, 0, width, 30, 370);
fill(0,255,0); //green
ellipse(x2, 125, 20, 20);
// map range (0-width) to (30-170)
float y1 = map(mouseX, 0, width, 30, 170);
fill(0,0,255); // blue
ellipse(10, y1, 20, 20);
}
Notes
